What is net income and why is it important for an individual or an organization to know what their net income is? Continue reading to find the details.
Approaching revenue is imperative to business development, however it does not paint the most precise financial image of your business. You should know whether your organization is benefitting in the wake of deducting operating expenses. You need to decide your business’ net income. In the event that you do not have income, you do not have a business. Yet, realizing your income alone will not give you an exact image of your business results.
You need to know whether your business is beneficial after deducting business expenses. That is the place where the income formula comes in. Computing your business’ total compensation encourages you to decide your business’ benefit, conclude whether to grow or lessen tasks, plan spending plans, and transfer data to financial backers. Keep on reading to figure out how to find net income, what net income is, and which financial statement to record your organization’s net income on.
What is net income?
Net income, likewise called net profit, is a computation that gauges the measure of the total revenues that surpass all out costs. At the end of the day, it shows how much revenues are left over after all costs have been paid. This is the measure of cash that the organization can keep for later use, take care of debt with, use to put resources into new activities, or convey to investors. Numerous individuals allude to this estimation as the reality since it by and large shows up at the lower part of the pay articulation.
Financial backers, leasers, and company management will in general zero in on the net income calculation since it is a decent pointer of the organization’s monetary position and capacity to oversee resources proficiently. Investors need to realize that their speculation will keep on being valued and that the organization will have sufficient money to deliver them a profit. Creditors need to know the organization if monetarily solid and ready to take care of its obligation with successful activities. The management of the company is regularly worried about both financial backers and credit concerns along with the organization’s capacity to pay salaries and rewards.
Understanding Net Income (NI)
Organizations utilize net income to ascertain their profit per share. Business experts regularly allude to net income as the bottom line since it is at the lower part of the income statement. Experts in the United Kingdom regard NI as beneficial for investors.
Net profits is perhaps the most essential estimation in accounting and finance. Clearly, higher benefits are quite often desirable over lower benefits. Organizations can utilize higher benefits to reinvest in new gear, wipe out debt, and even make payments to investors, however higher profits are not generally great.
Since organizations pay taxes on their benefits, it would bode well that the administration would attempt to limit profits on a tax premise to diminish the taxable income. This is the reason numerous organizations have a book to tax adjustment toward the end of every year. They need to change their book income to mirror certain assessment alternatives that are being exploited. For example, a few organizations may utilize LIFO for charge purposes and FIFO for book purposes to lessen the pay appeared on the tax return. Quickened devaluation is additionally utilized for a similar explanation.
On the other hand, numerous organizations are needed to meet certain profits every year to keep up credit agreements with their loan specialists. These pledges present an issue. On one hand, the board needs to show less benefit to diminish charges. Then again, they need to show more benefit to meet loan specialist’s prerequisites. This is the place where income and net profit can get controlled. Certain income acknowledgment rules can be applied freely to live up to the board’s desires. That is the reason it is imperative to peruse the fiscal summary commentaries and comprehend what estimations were utilized and how to find net income in the financial statements.
Calculating Net Income for Businesses
To find out the net income for a business, start with an organization’s total revenue. From this figure, take away the operational expenses and working expenses to compute the business’ profit before tax. Deduct tax from this sum to find the NI.
NI, as other accounting measures, is powerless to control through such things as forceful income acknowledgment or concealing costs. While putting together a venture choice with respect to NI, investors should audit the nature of the numbers used to reach the taxable income and NI.
Personal Gross Income vs. Net Income
Gross income alludes to a person’s total income or pre-tax income, and NI alludes to the distinction subsequent to calculating derivations and taxes into the gross income. To compute the taxable income, which is the figure utilized by the Internal Revenue Service to decide income tax, people who pay taxes take away allowances from gross income. A person’s NI is the difference between their taxable income and income tax.
For instance, an individual has $60,000 in gross pay and meets all requirements for $10,000 in deductions. That person’s taxable income is $50,000 with a strong tax rate of 13.88% giving an income tax payment of $6,939.50 and NI of $43,060.50.
Net Income on Tax Returns
In the United States, single taxpayers present a rendition of Form 1040 to the IRS to report yearly profit. This form does not have a line for overall gain. All things considered, it has lines to record gross income, adjusted gross income (AGI), and taxable income.
Subsequent to taking note of their gross income, taxpayers take away certain pay sources, for example, Social Security advantages and qualifying deductions, for example, student loan interest. The thing that matters is their AGI. Albeit the terms are utilized reciprocally, net income and AGI are two distinctive things.Taxpayers at that point subtract standard or organized deductions from their AGI to figure out their taxable income. As expressed earlier, the difference between taxable income and income tax is the person’s NI, yet this number is not noted on individual tax forms.
Net Income on Paycheck Stubs
Most paycheck stubs have a line solely for NI. This is the sum that shows up on an employee’s check. The number is the employee’s gross income, without the taxes, and retirement account commitments.
What is Revenue?
Before we get to how one can calculate net income, we need to have a clear understanding of the word ‘revenue’ and what it means. When we say “revenue,” we mean an organization’s all out receipts for a given period. This incorporates the actual measure of cash (money, checks, credit cards, and so forth) a business takes in, paying little mind to returns, discounts, and so on
Revenue, an organization’s “top line,” is something contrary to net income, the popular “bottom line” (of an organization’s pay articulation). This expression has entered normal discourse since net profit is the most ideal approach to look at productivity (however accounting terms may share immeasurably various implications for all common parlance and master use).
Each sort of negative exchange, even the basic return of a faulty item for another (ideally working) one, considers a cost. By following every single cost (in every single imaginable classification) you can precisely analyze your organization’s wellbeing and productivity. Put another way, revenue equals to gross income, yet not net income.
How to find Net Income?
Ascertaining your own net income may expect you to glance through old records and do a touch of math. It might appear to be overwhelming, however it is a lot simpler whenever you have decided on an interaction. Here are the means to take:
1. Determine your gross annual income
The absolute initial step is to locate your gross pay, or the aggregate sum of cash you acquire before allowances. It will fill in as a strong establishment for ascertaining your net income. Locate a past payroll interval’s compensation hit and find your deductions, if there are any. It should list everything before allowances. That would be your gross compensation for that period. Then, discover when and how regularly you get payment and increase that figure by the gross pay. For instance:
If you are paid $2,000 bi-weekly, multiply that number by 26.
Example:
Gross Pay x 26 = Gross Annual Income
$2,000 x 26 = $52,000
In the event that you are not salaried or work unpredictable hours, you should include every individual pay stub for the year. This will be the most practical strategy for acquiring a precise portrayal of your yearly income. In the event that you worked more than one job consistently (or simultaneously), guarantee that you consider every one of them.
2. Subtract deductions
The subsequent stage is to consider the entirety of your allowances and deduct them from your gross pay. Net income alludes to the pay after taxes, so you should take away allowances from your gross yearly income. When you eliminate the derivations, you will be left with your total taxable income.
Example:
Gross Income – Deductions = Total Taxable Income
$52,000 – $2,000 = $50,000
3. If applicable, deduct medical and dental
In the event that you have picked into any clinical and dental/vision inclusion, you can deduct those costs from your taxable income. To proceed with a similar example:
On the off chance that you had $50,000 total taxable income, take away your joint clinical and dental/vision coverage. Expect that the joint coverage is $500.
Example:
Total Taxable Income – (Medical + Dental) = New Total Taxable Income
$50,000 – $500 = $49,500
This data can vary depending on the situation. It is always suggested that you consult a professional if you have persistent questions and concerns.
4. If applicable, deduct retirement
In specific conditions, you might need to take away your individual retirement account (IRA) from your available pay. To proceed with a similar model:
In the event that after past derivations you had $49,500 in total taxable incme, deduct your IRA sum. Expect that the IRA sum is $1000.
Example:
Total Taxable Income – IRA Amount = New Total Taxable Income
$49,500 – $1000 = $48,500
5. Subtract what is owed
Whenever you have found your all out taxable income, you can take away the taxes you owe. You can begin by including all owed charges including government, nearby, state, federal retirement aide and Medicare. On the off chance that your boss takes out assessments, you will locate the absolute deductions on your compensation hits. Then, deduct taxes from your pay to decide your net annual income. To get done with a similar model:
You established that your gross pay was $52,000. You additionally found that you had $2,000 in deductions, $500 for protection inclusion (clinical + dental/vision) and $1000 for retirement. Presently, expect you have $3,000 in assessments.
Example:
Taxable Income – Taxes = Net Income
$48,500 – $3,000 = $45,500
Your net income for the year is $45,500.
How to find Net Income for the Month?
Net income is your organization’s absolute profits in the wake of deducting all operational expenses. A few people allude to net income as net earnings, net benefit profit or the organization’s ‘bottom line’. It’s the measure of cash you have left over to pay investors, put resources into new tasks or hardware, take care of debts, or put some aside for later use. The formula for calculating net income is:
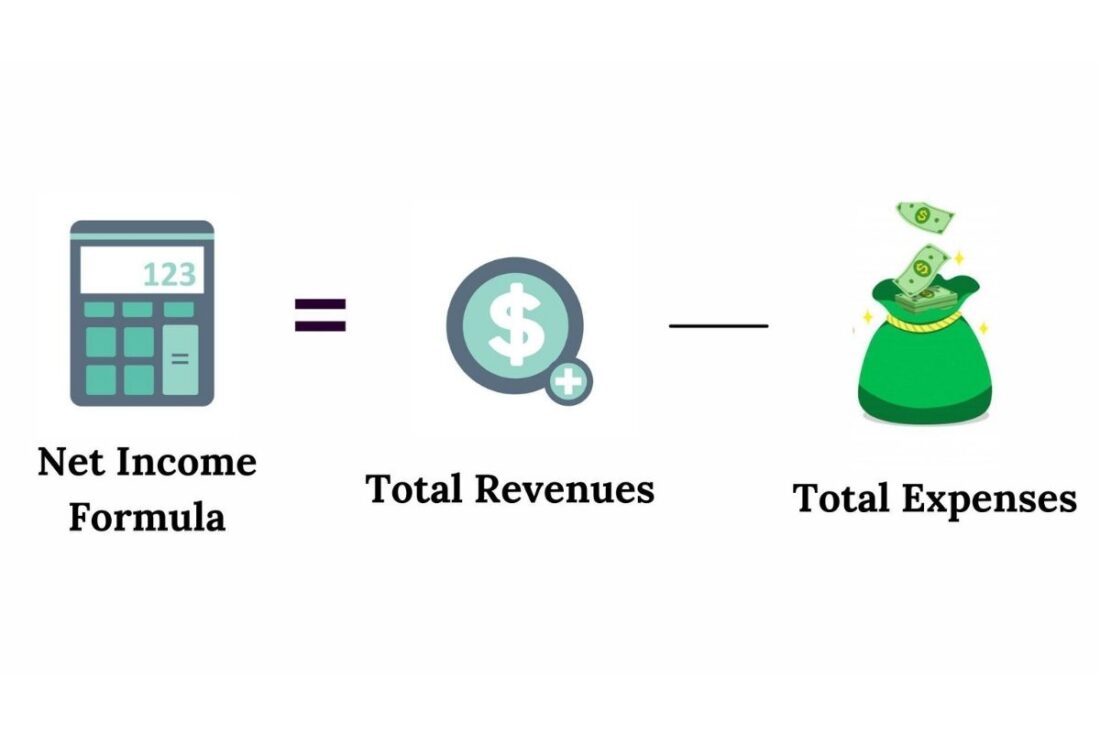
Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold – Expenses = Net Income
The initial part of this formula, ‘Revenue minus Cost of Goods Sold’, is also the formula for gross income. Therefore, the net income formula can also be put as:
Gross income – Expenses = Net Income
You can further simplify things, by expressing the net income formula as:
Total Revenues – Total Expenses = Net Income
Net income can be positive or negative. At the point when your organization has a larger number of revenues than costs, you have a positive net income. On the off chance that your complete costs are more than your incomes, you have a negative net income, otherwise called a net loss.
Utilizing the equation above, you can discover your organization’s total compensation for any given period: yearly, quarterly, or monthly – whichever time span works for your business.
How to find Net Income on Tax Return?
Net income is your gross pay minus the deductions and withholdings of your check. Your net income, some of the time called net pay or salary, is the sum that the check is composed for. It is the sum you would get on the off chance that you liquidated the check, or on the off chance that you utilize direct store, it’s the sum saved in your bank account.
Your gross income, regularly called gross pay, is the aggregate sum you are paid before deductions and retaining. On the off chance that you are not paid a yearly compensation, your gross compensation for a check will be equivalent to the quantity of hours you worked multiplied by your hourly pay rate. At the point when you include all your gross pay for a year, you ought to get your yearly gross income. In case you are salaried, the yearly compensation your manager pays you is equivalent to your yearly gross income.
You may see the expression “gross income” come up when documenting your annual duties.
For this situation, the vast majority utilize the term gross income to allude to your all out pay, which you can discover on Form 1040. All things considered, nontaxable sorts of pay are excluded from absolute pay. Nontaxable pay can incorporate blessing pay and pay utilized for certain retirement commitments.
You may likewise see the expression “net income” when recording personal charges. You can figure it utilizing data from your government expense form. Take your taxable income recorded on your Form 1040 (Line 10 for 2018) and afterward deduct your total tax (Line 15). The outcome is your net income dependent on your tax return.
What is Net Income in Accounting?
In business and accounting, net income (likewise complete far reaching pay, net income, net benefit, main concern, deals benefit, or credit deals) is a substance’s pay short expense of merchandise sold, costs, deterioration and amortization, interest, and charges for a period. It is figured as the leftover, all things considered, and gains over all costs and misfortunes for the time frame, and has likewise been characterized as the net increase in investors’ value that outcomes from an organization’s tasks. It is not the same as gross income, which just deducts the expense of products sold from income. For families and people, net income alludes to the (gross) income minus duties and other different deductions (for example required annuity commitments).
In shortsighted terms, net benefit is the cash left over in the wake of paying all the costs of an undertaking. Practically speaking this can get mind boggling in enormous associations. The clerk or bookkeeper should organize and apportion incomes and costs appropriately to the particular working extension and setting wherein the term is applied.
Net income is generally determined per annum, for each financial year. The things deducted will normally incorporate assessment cost, financing cost (premium cost), and minority premium. Moreover, favored stock profits will be deducted as well, however they are not a cost. For a marketing organization, deducted expenses might be the expense of merchandise sold, deals limits, and deals returns and recompenses. For an item organization, promoting, producing, and plan and advancement costs are incorporated. Net income can likewise be determined by adding an organization’s working pay to non-working pay and afterward taking away assessments.
The net profit margin is a connected proportion. This figure is determined by isolating net benefit by income or turnover, and it addresses productivity, as a rate.
Where to find Net Income on Financial Statements?
Net income (NI) is known as the “bottom line” as it shows up as the keep going line on the pay proclamation once all costs, interest, and assessments have been deducted from incomes. Some pay proclamations, notwithstanding, will have a different area at the base accommodating starting held profit with finishing held profit, through net income and profits.
Net Income VS Net Profit
As referenced above, individuals regularly allude to net income as net profit or “the bottom line.” Net pay and net benefit mean something very similar – yet numerous new money managers discover this equivalency befuddling. The stunt is this: there are numerous sorts of a benefit, yet just net benefit approaches pay. From another point: overall gain approaches net benefit, however total compensation doesn’t rise to benefit, as a rule. For example, a roma tomato is a similar size as a kiwi natural product, however not a wide range of natural products. Unquestionably, a watermelon overshadows a roma tomato. So, benefit, similar to “natural product” is an overall term, which can make disarray when we allude to it nonchalantly. To discuss obviously with other financial specialists, consistently indicate the sort of benefit to which you’re alluding.
The 3 Kinds Of Profit:
1. Enhancing Company Profitability with Gross Profit Analysis
To gain a fundamental understanding of your company’s profitability, utilize this straightforward formula:
Calculate Gross Profit by deducting Cost of Goods and Services from Net Sales.
Net Sales represent revenue from product and service sales, excluding investment and asset income. Ensure to subtract discounts and allowances from this total. Cost of Goods and Services (COGS) encompasses direct expenses incurred in product or service development. Lowering this expenditure can significantly boost your bottom line.
For instance, negotiating with suppliers and scouting for the best prices on raw materials can reduce costs. In your organic feline toothpaste venture, this involves securing optimal deals on vegetables and meats from local farmers and procuring coconut oil, a firming agent in your toothpaste, in bulk quantities to reduce resource expenses.
Evaluate the effectiveness of discounts and other marketing incentives offered to new customers. Do they align with your projected growth figures? Are you overspending or underspending? Are discounts primarily aimed at clearing excess inventory?
2. Operating Profit
If you are interested in finding out the true health of your business, analyze your company’s operating profits using these two methods:
EBIT – Earnings before Interest and Taxes
EBITDA – Earnings before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization
The idea is to isolate the cash you make by means of creation and deals from all your organization’s other monetary exercises. By deducting your inconsequential costs, you can decide the accomplishment of your center capacities: creation, overhead, deals/advertising, compensation/pay rates, and so on
To get a business credit, you will need to give working benefit numbers. Your money lender will contrast your Operating Profit Margin with the size of your business to decide your solidness. You likely need a high edge for your specialty business.
For instance, in the event that you sell not many feline toothpaste tubes at store costs, you can get by on a lower volume of deals. Just huge, large box retailers (with gigantic deals volume) can stay productive on thin edges.
3. Net Profit
After you have set apart all your company’s expenses(interest, taxes, amortization, depreciation, etc.) from your net sales, you can then figure out your net profit/net income:
Net Profit/Net Income = Gross Profit – (Total Operating Expenses + Interest + Taxes + Amortization + Depreciation)
When somebody asks you, “Is cat toothpaste truly productive? What’s your primary concern?” give them the figure you got from the (fairly enormous) recipe above. Investors, sellers, and different partners need this data to get a clear image of your operational wellbeing.
That being said, most money managers comprehend new companies need time to arrive at benefit. A financial backer in your feline toothpaste organization may surely know that you intend to lose cash pulling in clients in the initial 2 years and make your benefits in years 3 to 5.
This individual may well take your client base figures more to heart than your main concern. However long you’re on target to productivity and meet your objectives, you can in any case pull in the capital you need to make headway.
Along these lines, compute net gain, comprehend the different sorts of benefit, and give your partners the most ideal data – confiding in your organization’s continued sales and market share development!
Importance and Uses of Net Income
- Net income is the most sought after number in the budget report of a Company.
- A ton of monetary proportions are affected by the net income number. Investors definitely follow this measurement as the measure of profit paid to the investors relies upon the total compensation procured by the Company.
- Albeit net income is a significant measurement as far as benefit acquired by the Company is not the genuine money procured by the Company. The assertion of activities or the benefit and misfortune articulation of the Company incorporates a great deal of non-money things, for example, deterioration and amortization. Subsequently, any adjustment in the overall gain or the monetary proportions, in that capacity, ought to be appropriately investigated.
- Lower net income might be because of a ton of variables, including helpless deals, helpless administration, high costs, and so forth
- Net income changes from Company to Company and industry to industry. It can change because of the size of the Company and the business where it works. A few Companies have hefty resource plans of action; subsequently, the deterioration costs will be high while others may have light resource models. Further, development factors in businesses, obligation levels, government charges influence the net gain quantities of the Company.
Conclusion
Net income, also known as net profit, represents the difference between sales and various expenses such as cost of goods sold, operating expenses, depreciation, interest, and taxes. Investors find this figure crucial for assessing a company’s profitability, as it reveals how much revenue exceeds expenditures. This vital metric is prominently featured on a company’s income statement, serving as a key indicator of its overall financial health.